Why Your Brain Loves Pictures
The Science Behind Babbly's AI-Powered Flashcards
You can effortlessly recall faces you've seen years ago, yet forget new words just hours after learning them. The secret lies in the way your brain processes information: images create some of the most powerful and enduring memories. Babbly's AI-driven visual flashcards harness this natural advantage by linking words directly to strong mental images. So when you see perro, your mind instantly pictures a dog—no need for mental translation. It's like having a visual dictionary that keeps up with your thoughts.

How Your Brain Really Learns
The Visual Memory Advantage


Your Brain is a Visual Processing Machine
Here’s an eye-opening fact: your brain handles visual information 10 times faster than text. While you’re still reading the word elephant, your brain has already recognised, categorised and understood a picture of one.
This isn’t by chance—it’s how we’ve evolved. For millions of years, human survival relied on the ability to instantly spot visual cues: Is that rustling bush hiding a predator? Are those berries safe to eat? Your visual processing is designed to be lightning-fast and incredibly reliable.
The numbers speak for themselves:
- You can process a visual scene in as little as 13 milliseconds
- You remember 65% of visual information after three days
- You remember only 10% of text-only information after the same period
- Visual memories can last decades even with minimal reinforcement



The Dual-Coding Revolution
In 1971, psychologist Allan Paivio discovered something that transformed how we understand memory for good. His Dual-Coding Theory showed that your brain doesn’t just store things one way—it actually has two types of memory systems that are connected but distinct:
The Verbal System:
- Handles words, sounds and language
- Works step by step (one word after another)
- Mainly located in your brain’s left hemisphere
- Perfect for logic and sequential thinking
The Visual System:
- Handles images, colours, and spatial relationships
- Processes information in parallel (lots at once)
- Centred mainly in your brain’s right hemisphere
- Excellent for recognising patterns and making emotional connections
Here’s the magic: When you learn using both systems at the same time, your brain builds two separate pathways to the same information. It’s like having a backup route—if one’s blocked, the other will still get you there.

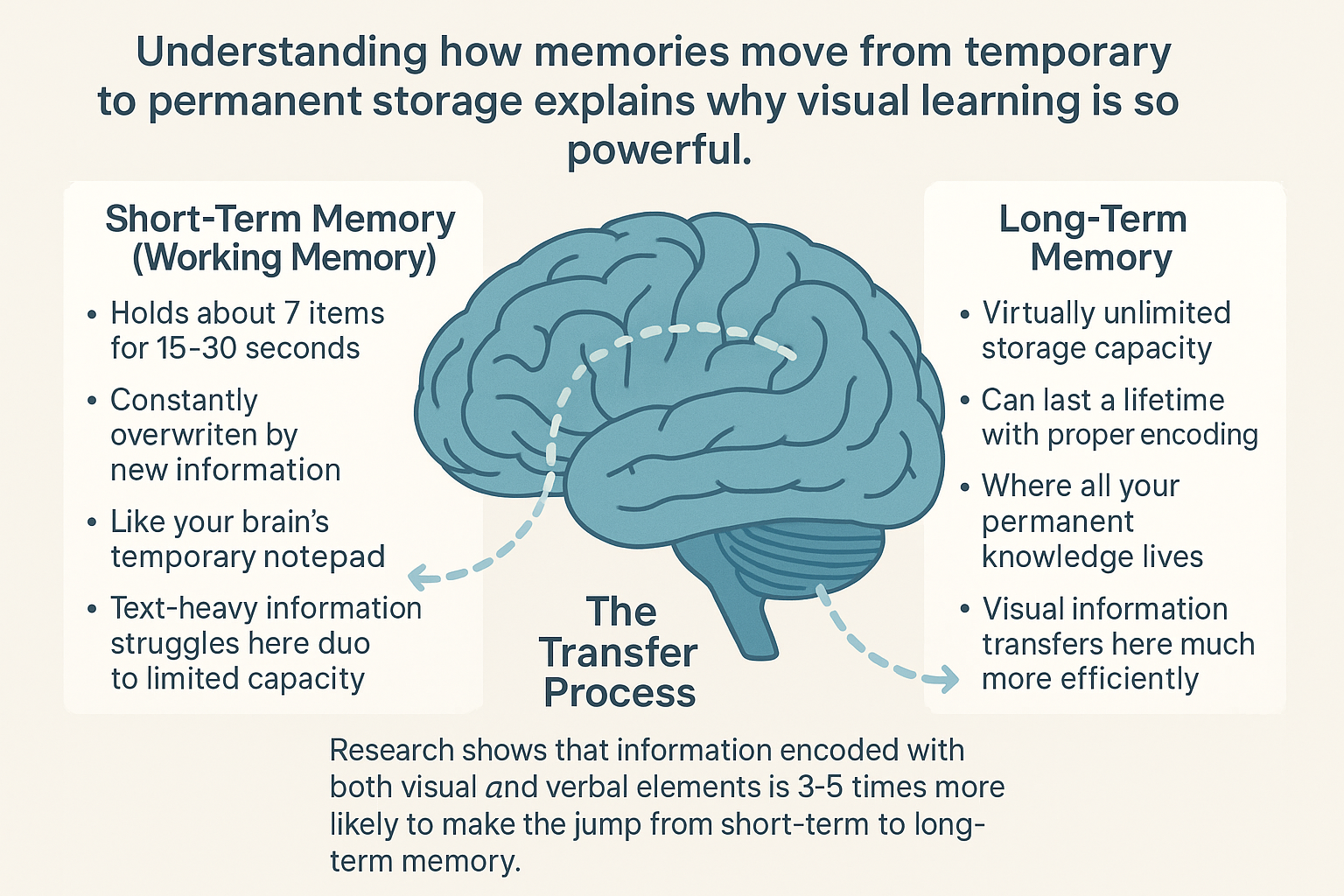

Short-Term vs. Long-Term Memory: The Visual Highway
Understanding how memories move from short-term to long-term explains why visual learning is so powerful.
Short-Term Memory (Working Memory):
- Can hold around 7 pieces of information for 15–30 seconds
- Constantly updated as new info comes in
- Like your brain’s scratch pad
- Struggles with text-heavy input due to limited capacity
Long-Term Memory:
- Almost unlimited in capacity
- Can store knowledge for a lifetime, if encoded well
- Home to everything you truly know
- Visual input moves here much more effectively
The Transfer Process: Studies show information which mixes visual and verbal elements is 3-5 times more likely to transfer from short-term to long-term memory. That’s why you can remember a film scene far better than a textbook paragraph, and a single photo can instantly transport you back in time.

The Translation Problem
Why Going Through Your Native Language Slows You Down


The Hidden Cost of Mental Translation
Most language learning methods force you into a slow and clumsy routine:
Spanish Word → English Translation → Mental Image → Understanding
"perro" → "dog" → 🐕 → understanding
This three-stage loop might look reasonable, but it actually causes major problems:
- 1. Processing Delays: Every extra step takes time. Instead of instant recall, your brain has to run its own mini translation service. During real conversations, this lag makes you sound hesitant and less natural.
- 2. Cognitive Overload: Your working memory can only cope with so much. Juggling translation, categorising and memorising at once means something has to slip—usually the very words you’re trying to learn.
- 3. Translation Dependency: The more you rely on your native language as a bridge, the more you get stuck needing it. You begin to think in English and convert to Spanish, instead of just thinking in Spanish.
- 4. Cultural and Contextual Loss: Languages aren’t just swapped-out words—they reflect different ways of thinking. Translate everything through your native language and you’ll miss out on unique cultural meanings and the richness that makes each language special.



The Direct Path: Visual Learning Without Translation
Babbly takes away the translation barrier entirely:
Spanish Word → Visual Image → Direct Understanding
"perro" → 🐕 → instant understanding
This straightforward approach has big benefits:
- Faster Processing: Your brain recognises images almost instantly. There’s no delay, no going back and forth.
- Stronger Memory: Linking words directly to images builds robust brain pathways—far stronger than word-to-word translation.
- Truly Natural Thinking: You start thinking straight in your new language, with no need to mentally translate every time.



Real-World Examples of Translation Problems
Example 1: "Bread" vs "Pan"
- The English word bread probably makes you think of soft sandwich loaves
- The Spanish word pan covers a long list—baguettes, rolls, tortillas and more
- Direct visual learning helps you see real types of Spanish bread, not just an English loaf with a Spanish label
Example 2: "Blue" vs "Azul"
- English uses just one word: blue
- Spanish makes distinctions, like azul (regular blue) and celeste (sky blue)
- Visual learning lets you naturally notice these subtle differences

The Science Behind Visual Learning

Research shows time and again that people can recall 83% of images they see—even for just a moment—compared to just 10% for text alone after three days.

Students using a mix of images and words perform 89% better than those using just text. This isn’t just theory—the evidence holds up across thousands of learners and many different studies.

fMRI scans reveal visual learning triggers multiple parts of the brain at once, building what scientists call elaborative encoding—lots of pathways to each memory, making it much harder to forget.